What is Noun in English Grammar with Description & Example
What is noun ?
(What is Noun in English Grammar with Description & Example) If you’ve ever asked yourself, “What exactly is a noun?” then you’re in the right place. In the simplest terms, a noun is a naming word. It gives names to the people, places, things, animals, and even abstract ideas around us. Without nouns, language would lose its meaning because we wouldn’t be able to identify or talk about anything.
Think about it—every single object, person, or concept you come across in daily life has a name, and that name is a noun. For example:
- Person: Teacher, doctor, Mary, John
- Place: School, park, London, India
- Thing: Book, table, pen, computer
- Animal: Dog, cat, elephant, tiger
- Idea: Love, freedom, honesty, courage
Nouns also play an important role in sentence structure. They often act as the subject (who or what the sentence is about) or the object (who or what receives the action). For instance:
- The dog barked loudly. (Here, “dog” is the subject.)
- She loves music. (Here, “music” is the object.)
In short, everything in the universe that has a name can be called a noun. From the chair you sit on to the emotions you feel, nouns are everywhere!

Classification of Nouns
First, I’ll give you a roadmap, and then I’ll explain everything to you step by step with examples. In English grammar, nouns are broadly classified in two ways:
A. On the basis of meaning its two type.
- Proper Noun
- Common Noun
B. On the basis of form Common Nouns are two type.
- Countable Noun
- Uncountable Noun
Again Common Noun is classified in to 3 type
- Collective Noun
- Concrete nouns or Material Noun
- Abstract Noun
Let’s understand each in detail with roadmap and examples.

1. What is Proper Noun ? (Explaining with eamples)
(What is Noun in English Grammar with Description & Example) A proper noun refers to the specific name of a person, place, organization, or thing. It always begins with a capital letter.
Examples:
- Rahul is my best friend. (Person)
- New Delhi is the capital of India. (Place)
- The Times of India is a popular newspaper. (Organization)
NB: Always remember — proper nouns are unique and particular.

2. What is Common Nouns ? (Explaining with examples)
A common noun is a general name given to a class of people, animals, places, or things. Unlike proper nouns, they are not capitalized unless they start a sentence.
Examples:
- The boy is playing in the park. (Person)
- She bought a new car. (Thing)
- The city was full of lights. (Place)
NB: Always remember —- Common nouns are shared by many and are not unique.

Common Noun: Number (Based on their form)

A. What Are Countable Nouns?

Countable nouns are the names of things we can count easily. If you can say one, two, three, or put a number in front of it, then it is a countable noun. For example: one apple, two apples, and three apples.
Countable nouns are divided into two forms:
- Singular Countable Nouns. (Used when talking about just one item)
- A book
- A pen
- A chair
- An apple
- Plural Countable Nouns (Used when talking about more than one item.)
- Two books
- Three pens
- Four chairs
- Many apples

B. What Are Uncountable Nouns?

For example: water, milk, sugar, rice, information, advice, happiness.
Unlike countable nouns, uncountable nouns do not have plural forms. You cannot say waters or milks in everyday usage. Instead, they remain in the same form, whether you are talking about a small amount or a large quantity.
(What is Noun in English Grammar with Description & Example)
This is why uncountable nouns do not follow the singular-plural concept. Instead, we use words like some, much, a little, a lot of, or less to describe their quantity. For instance:
Some rice (not rices)
Much information (notinformations)
A little sugar (not sugars)

Common Noun (Based on their meaning)

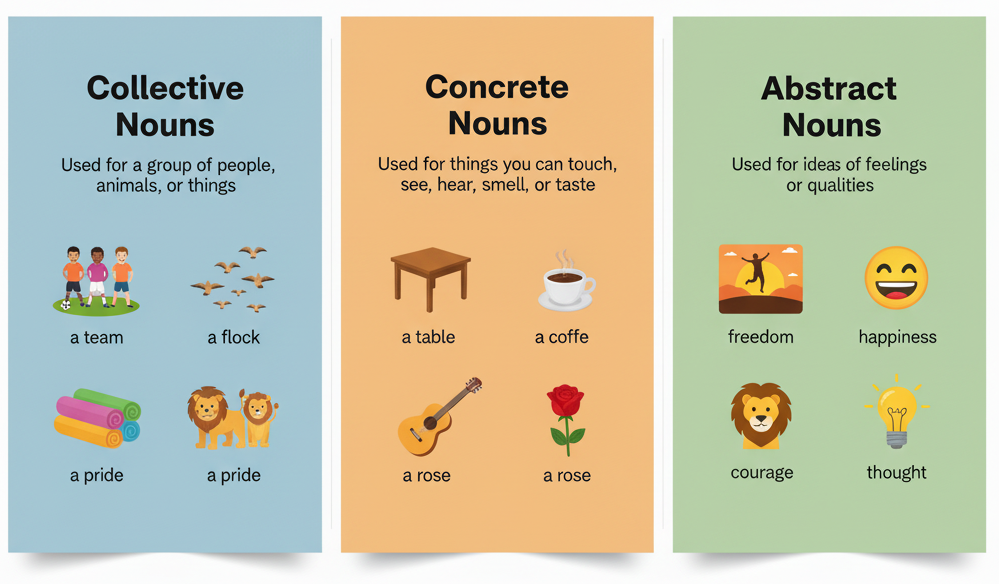
1.Collective nouns:

Collective nouns refer to common nouns representing a gathering or collection of people or objects sharing a similar kind or category. Examples include “team,” “herd,” or “flock,” conveying unity among individuals or items of a particular type..
Example:
- Our class took a field trip to the park.
- A flock of birds flying in the sky.
2. Concrete nouns or Material Noun :
A concrete noun is a word for something real and touchable, like things you can taste, touch, or see. It’s about things that exist physically in the world.
Example:
- The house at the end of the street belongs to me.
- My dog likes to eat bread.
3. Abstract Noun:
Abstract nouns are words for things we can’t touch, like feelings or ideas. They’re about stuff we think or feel, not things we can see or touch, like love or freedom.
Example:
- Man has both good sides and evil sides.
- Ram has a fear for dogs.
- They Love each other
Compound Noun & It's Examples.
What is Compound Noun?

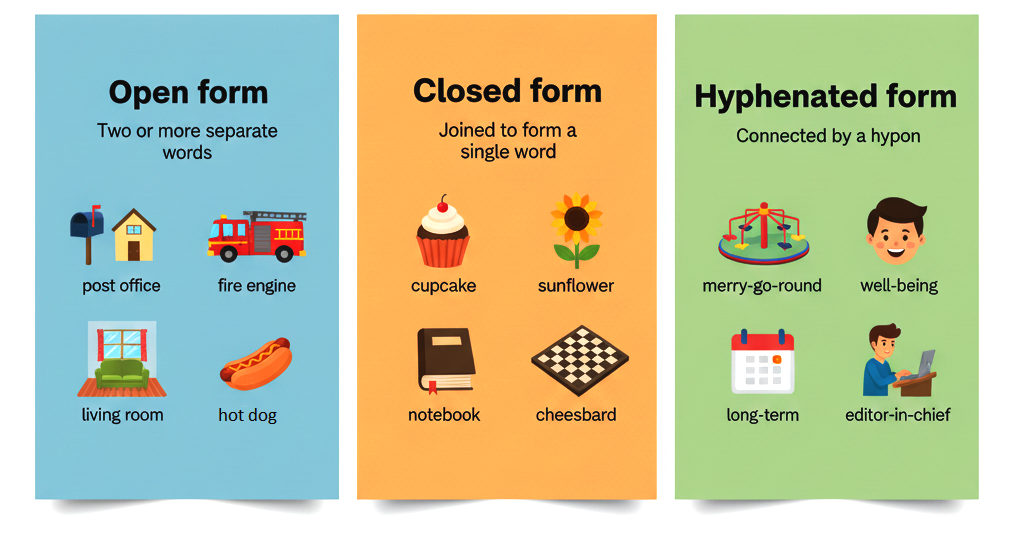
Compound nouns combine two or more words, creating a single entity. These compound words can be crafted in three different ways, showcasing the versatility and flexibility of language.
❖ Open form
❖ Closed form
❖ Hyphenated form
❖ Open form:
Compound nouns are special words that act as one, even though they’re written as two or more words with spaces between them.
Example:
- Post office
- Middle class
❖ Closed form:
It’s when two words come together to form a single word without any punctuation or spaces.
Example:
- Baseball
- Keyboard
❖ Hyphenated form:
In this, two or more words are linked by a hyphen to create a compound word.
Example:
- Eight-pack
- Brother-in-law
Possessive Nouns and It's Example
What Is a Possessive Noun?
A possessive noun answers the question “Whose?” Possessive nouns are used to show ownership or possession. They tell us that something belongs to someone or something. In the other hand we can tell possessive nouns make sentences clear and meaningful by showing relationships of ownership.
For example:
Ram’s car → The car belongs to Ram.
Students’ books → The books belong to the students.
In English grammar, we usually make possessive nouns by adding an apostrophe (’) and the letter “s” to the end of a noun.
Here are the main rules for forming possessive nouns in English:
- Singular Noun + ’s
Add ’s to a singular noun.
Ram → Ram’s car
Dog → Dog’s bone
Girl → Girl’s dress
- Plural Noun Ending in “s” + ’
If the plural noun already ends in “s”, just add an apostrophe (’) after it.
Students → Students’ books
Teachers → Teachers’ meeting
Dogs → Dogs’ owner
- Irregular Plural Nouns (Not Ending in “s”) + ’s
Some plural nouns don’t end with “s”. In that case, add ’s.
Children → Children’s toys
Men → Men’s room
Women → Women’s clothes
- Names Ending in “s”
Both are acceptable:
James’s car
James’ car
(Use James’s for clearer pronunciation.)
- Compound Nouns
Add the apostrophe to the last word in the compound.
My sister-in-law’s bag
The editor-in-chief’s office
- Joint and Separate Possession
Ravi and Rina’s house → One shared house.
Ravi’s and Rina’s houses → Two separate houses.
When to Use “of” Instead of Apostrophe (’s)
We usually use “of” for non-living things or longer phrases.
The roof of the house (instead of the house’s roof)
The colour of the sky
Noun Gender in English Grammar – Definition
What is Gender Noun ?
Definition of Noun Gender: In English grammar, gender is a classification of nouns and pronouns based on the sex or characteristics of the person, animal, or thing they refer to. It helps us understand whether the noun is masculine, feminine, common, or neuter.
Although English is less gendered than some other languages (like French or Hindi), gender still plays an important role in grammar, especially when using pronouns such as he, she, or it. Gender is the form or category of a noun that shows whether it refers to a male, female, both, or neither.
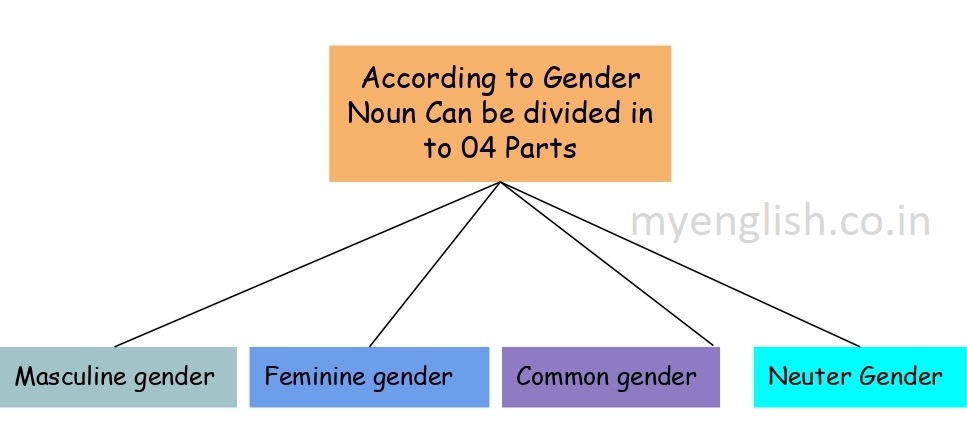
According to Gender Noun can be divided in to 4 parts. Follow the structure below to get more information. (What is Noun in English Grammar with Description & Example)
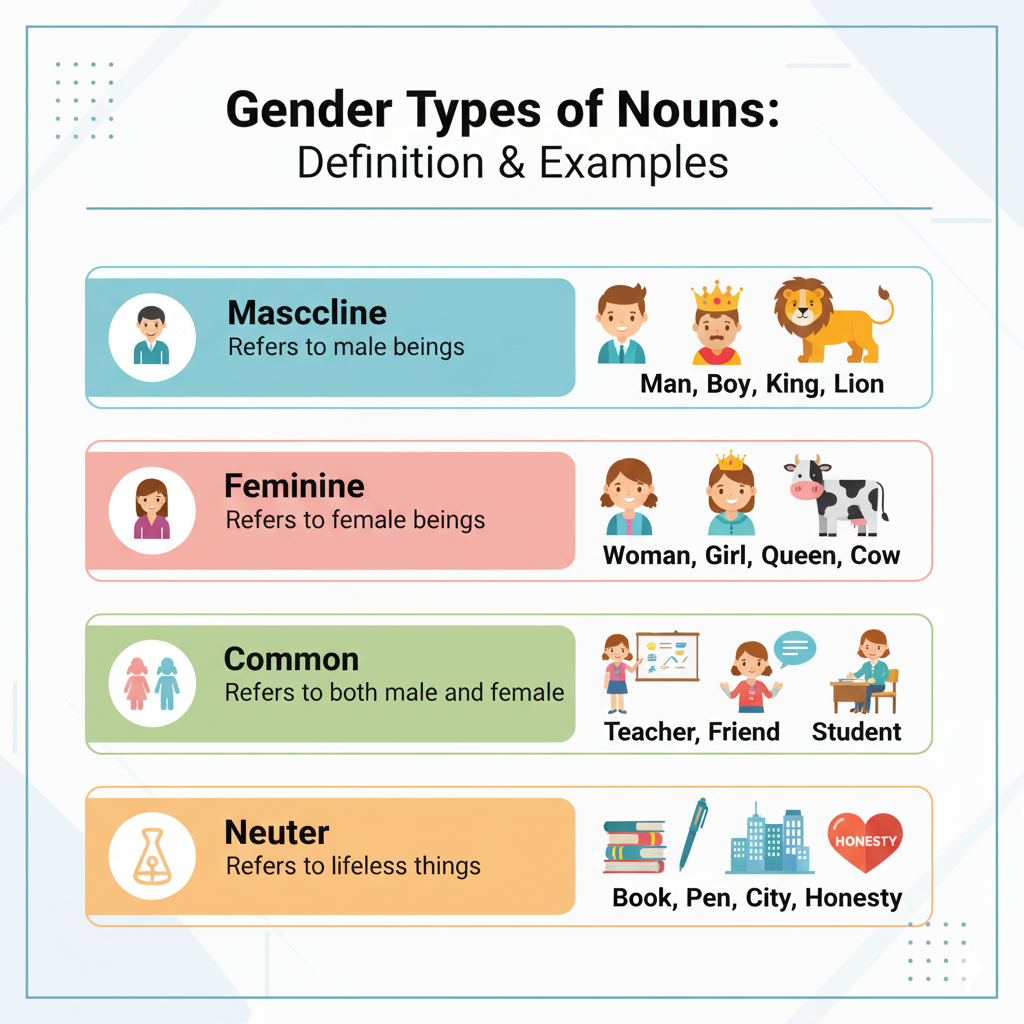
- Masculine Gender: Masculine gender refers to male living beings — men, boys, and male animals.
Examples: Man, Boy, King, Father, Uncle, Bull, Lion, Rooster
Example Sentences:
The king ruled the kingdom wisely.
A boy is playing in the park.
- Feminine Gender: Feminine gender refers to female living beings — women, girls, and female animals.
Examples: Woman, Girl, Queen, Mother, Aunt, Cow, Lioness, Hen
Example Sentences:
The queen addressed her people with grace.
A mother loves her child unconditionally.
- Common Gender : Common gender refers to nouns that can represent both males and females.
The gender is not specified — it can be either a man or a woman.
Examples: Teacher, Student, Friend, Doctor, Baby, Child, Cousin, Leader
Example Sentences:
The teacher is explaining the lesson.
My friend is coming to visit today.
(Here, we don’t know whether the friend is male or female.)
- Neuter Gender : Neuter gender refers to non-living things that have no sex.
These include objects, materials, places, or ideas.
Examples: Book, Table, Pen, Computer, Tree, Car, City, Honesty
Example Sentences:
The book is on the table.
Honesty is the best policy.
How Gender Changes in Nouns
Sometimes, nouns change their form or spelling to show gender differences.
a) By Adding a Suffix
Actor → Actress
Waiter → Waitress
Prince → Princess
Hero → Heroine
b) By Changing the Word Entirely
Man → Woman
King → Queen
Boy → Girl
Husband → Wife
c) By Using Different Words Before or After
He-goat → She-goat
Bull-calf → Cow-calf
Peacock → Peahen
Tips to Remember
Masculine → Male beings
Feminine → Female beings
Common → Both male and female
Neuter → Non-living things
Conclusion of English Nouns
Dear all I know that here conclusion may not seem necessary for this topic, I want to ensure every learner truly understands the importance of nouns in English. Nouns are the building blocks of the language because they give names to people, places, animals, objects, and ideas. Without nouns, we wouldn’t be able to identify anything or communicate clearly about the world around us.
By learning how nouns are classified — based on their meaning, number, gender, and form — students can use them correctly in sentences. When you understand different types of nouns like proper and common nouns, countable and uncountable nouns, abstract and concrete nouns, and gender forms, you become more confident and accurate in expressing your thoughts in English. (What is Noun in English Grammar with Description & Example)